Ensuring you use the correct cables is essential in various situations, both at home and in the office, and data centre cabling is no exception. Cable management in a work environment is crucial, not only for staff safety but also so employees can complete work efficiently.
Fibre optics offer numerous options for data centres, each intended for different business types and requirements. They are essential to data centres, keeping them secure and reliable.
Whilst all organisations needing IT infrastructure for their business should have data centre solutions, they are especially vital for commercial buildings, such as warehouses and offices.
Fibre optics can play an essential role in these solutions, allowing high levels of data transportation to keep work flowing as it should.
But what are these solutions, and what do they do?
Here are four fibre optic data centre solutions for your business.
What Is A Data Centre?

Offering a range of computing services within a business, a data centre is a part of or an entire building that contains various IT infrastructures, such as storage devices and computer systems. They store data, process it and distribute it via the Internet.
Data centres vary in size, depending on what is required. For example, larger companies, such as Amazon or Google, will need data centres on a larger scale. They contain various electronics surrounded by equipment like power cables.
In these environments, servers and the Internet are connected via routers, whereas you usually store the data on hard drives. The type of router and other equipment, such as the servers and hard drives, are used for speed purposes as a data centre needs to be both fast and reliable.
Fibre Optic Solutions for Data Centres
1) Server Racks
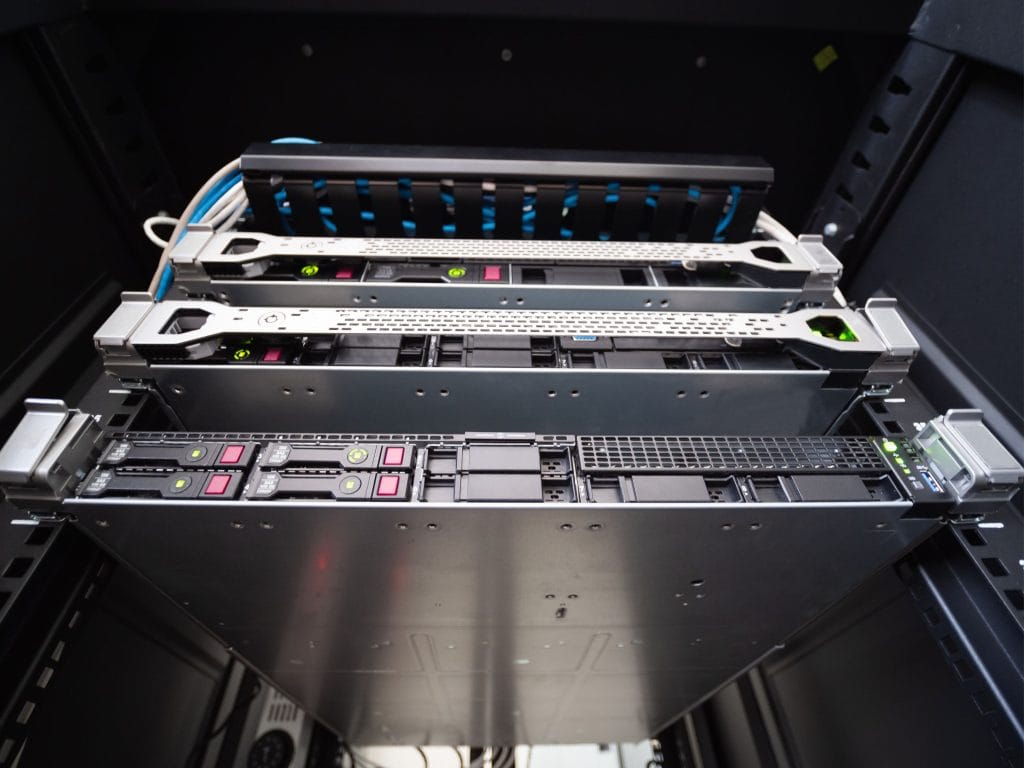

This solution holds computing equipment, such as servers, cables and networking devices.
However, you can use some server racks for other things, such as cooling systems and telecommunication equipment. These racks can also house networking equipment and uninterruptible power supplies (UPS).
A server rack, called a chassis, is a framework made of electronics and steel. The rack has a systematic design and usually has standardised dimensions to help you store the usual IT equipment sizes. You can install multiple server racks in a standard enclosure and keep numerous stacked servers here.
These racks enable the organised storage and management of IT equipment whilst keeping them secure. Each rack contains slots for electrical, Internet and networking cable connections.
The amount of equipment a server rack can house, specifically through its number of slots or capacity, classifies the chassis.
2) Fibre Optic Containment
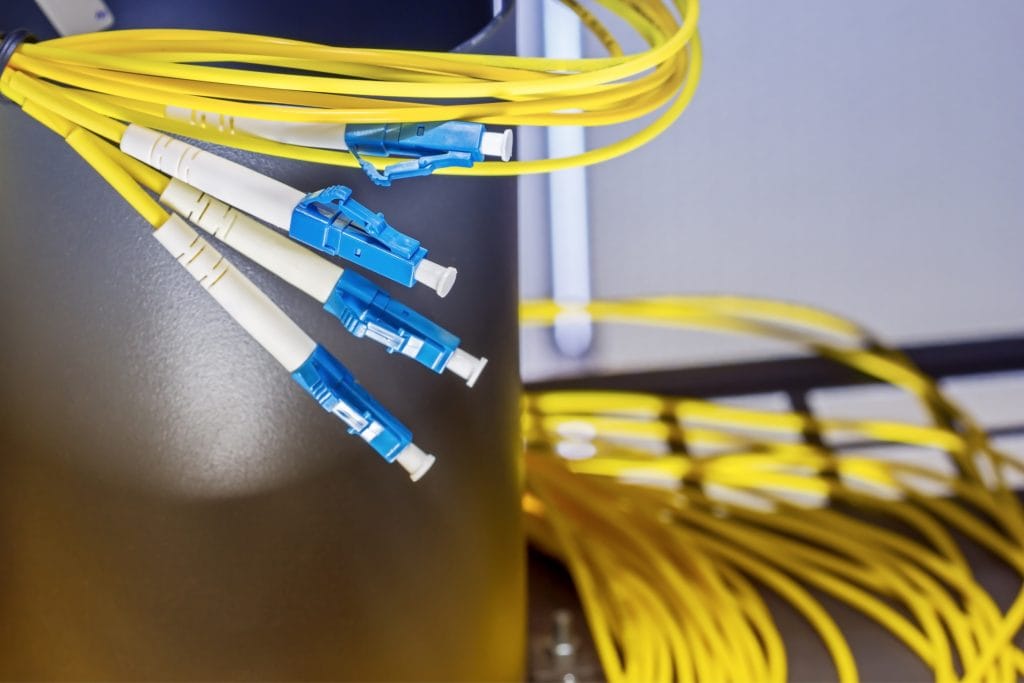

This solution protects the fibre optic cables used within the data centre, such as breakout cables. Fibre optic containment allows the cable to follow a logical path in a neat and tidy manner. There are various fibre containment types, so you can find the one that best suits your business and data centre.
Usually, the system contains the following components:
- Cable trays
- Conduit
- Fibre enclosures
- Patch panels
- Raceways
The fibre enclosures and patch panels provide the fibre terminations with protection and connectivity, whereas the cable trays, conduit and raceways organise and route the cables. The fibre containment’s construction and design ensure the data centre operates accurately and correctly.
When selecting fibre containment, such as cassettes, there are several elements you must consider. These systems must meet industry standards for various codes and regulations to protect the optical fibres, such as ensuring band radius is met.
Fibre optic cables are in semi-rigid tubes, which allows the fibre to remain as it is while the tube stretches around it.
Cable density is also essential, as you must manage the cables without causing more interference and congestion than necessary. Data centres contain various equipment and servers, so it is crucial to route cables to avoid these issues.
Fibre cables are fragile, so you must protect them to minimise the chances of breakage. When installing fibre optic cables, you must check the manufacturer’s specifications. Each cable has a different minimum bend radius, the smallest bend curvature required for the cable to remain intact. Not following these specifications can lead to irreparable cable damage or loss of data.
Usually, the recommended minimum bend radius for a cable is 20 times the cable’s diameter when under tension, whilst ten times the diameter after installation and under no tension.
However, this is not always applicable, so follow the cable’s specifications.
3) Cable Management

Maintaining fibre optic cables in a data centre is essential, so cable management systems are vital. They enable easy access to cables, such as trunk cables, for maintenance and upgrades when required.
However, cables must be organised to minimise disruptions to other cables if any need replacing, removing or adding, which helps reduce and prevent data centre downtime. There should also be space for the cables, as they may require time to cool down so the equipment can perform as it should.
Cable management can include various elements, such as using cable ties and labelling the cables, and can also involve software to manage the routing. Cable ties enable you to bundle the cables together.
This management can include horizontal cable management, vertical cable management and hook and loop straps. You must find the system or systems that suit your data centre, as each is unique and has different requirements.
The bend radius is not just to be considered for fibre optic containment. When managing your optical fibres, keep it in mind and try to minimise bends where possible.
4) Backup and Recovery Solutions
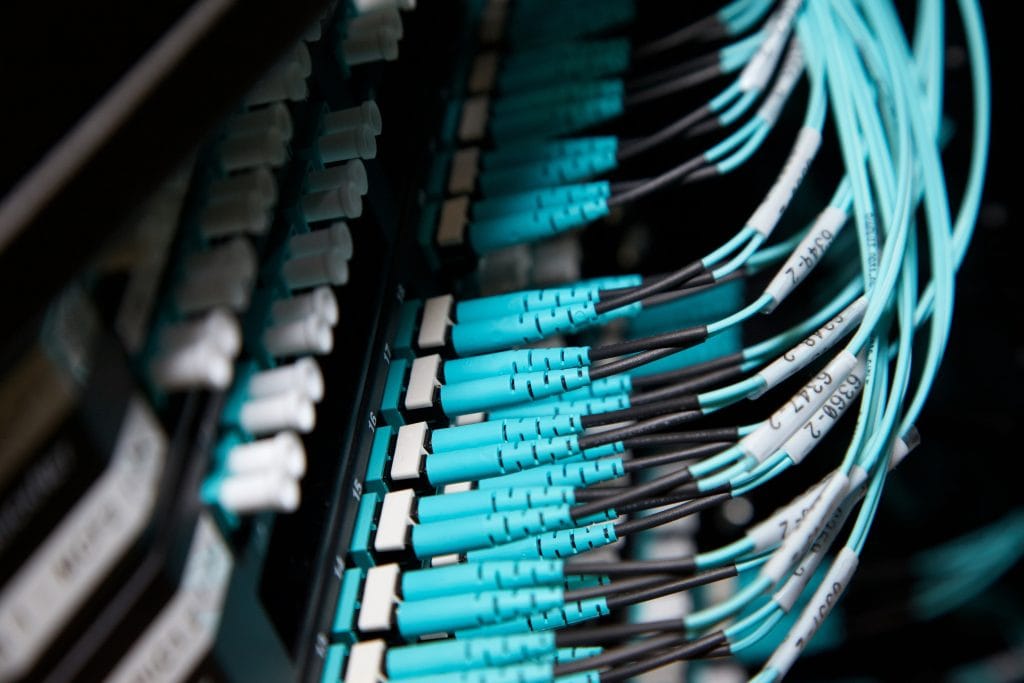

If a system fails, you can potentially lose data. Therefore, data centres must have backup and recovery solutions to protect that data if a disaster occurs.
There are various backup and recovery solutions, but usually, the business backs the data up at a separate location. This solution enables you to restore the data if necessary. The second location can but doesn’t have to be a cloud-based storage service.
Data centres use various devices to manage data traffic and keep it secure. This applies to the traffic within the data centre and between numerous locations. Some of these products include firewalls, routers and switches.
Featured Product: OS2 Breakout Cable
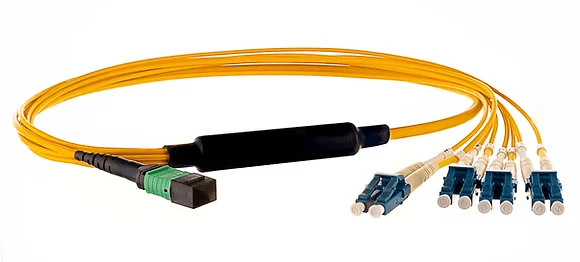
Ideal for industrial settings, breakout cables use multiple fibres, each with its own jacket, and these fibres are then collectively encased in another layer. The OS2 breakout cable has several LC connectors at one end and an MTP/MPO Female connector at the other, and it is well-suited for data centres that need to save space and manage cables.
Data centres require the correct solution for their unique needs, and a data centre cable specialist can help you find what you are looking for. After reading this blog, you should have more information about which solution you can use, but if you have more questions, Altimex can help you find the answers.
Contact us for more information, product quotations, and to resolve your fibre optic solutions enquiries.


