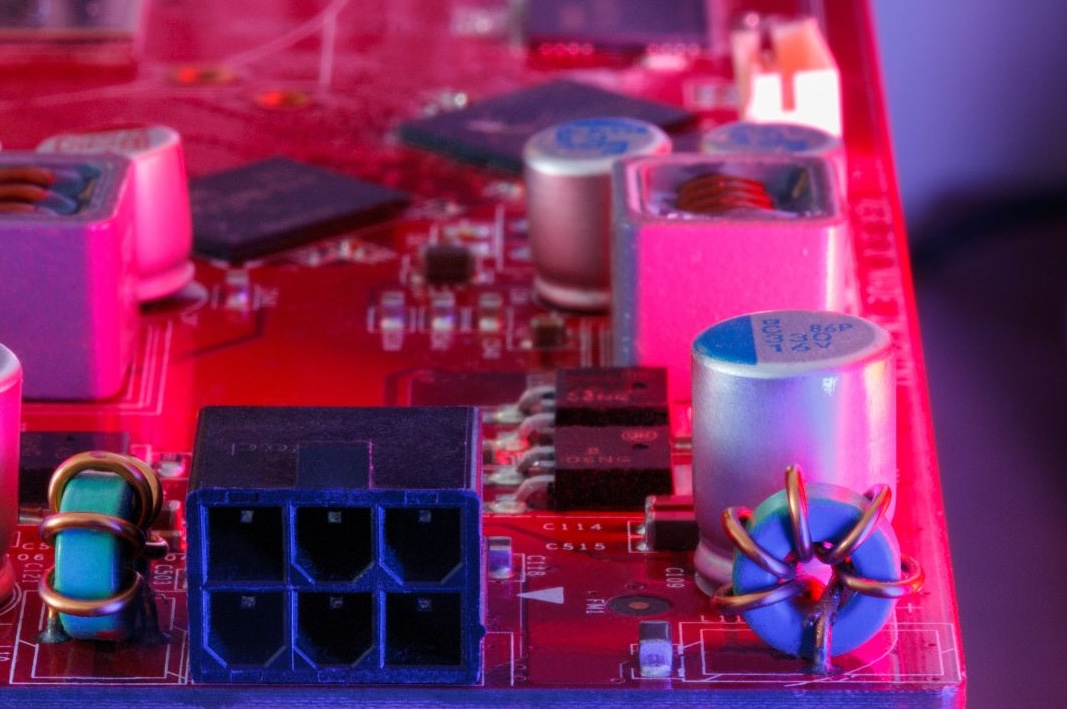
Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) are pivotal in consumer electronics, serving as the backbone for integrating sophisticated circuits.
This article explores common devices that utilise PCBs in electronics, offering electricians, engineers, and product designers essential insights into their indispensable role in modern electronic design.
1. Mobile Phones

PCBs in mobile phones epitomise advanced engineering, tailored for the devices’ slim form through intricate miniaturisation.
Utilising multilayer designs, these PCBs efficiently manage complex circuitry in limited spaces, integrating processors, memory, and connectivity modules.
High-density interconnector (HDI) technology and surface-mount technology (SMT) enable higher functionality and compactness.
This sophisticated approach ensures mobile phones meet the demands for performance, power efficiency, and reliability, showcasing the indispensable role of modern PCBs in consumer electronics.
2. GPS Units
Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) in GPS units are central to integrating essential components for GPS functionality into a cohesive system.
These PCBs manage complex signal processing tasks to accurately extract location data from satellite signals, employing advanced miniaturisation techniques to accommodate intricate circuitry within compact devices.
Additionally, PCBs in GPS units are engineered to ensure signal integrity and withstand environmental challenges, making them vital for the reliable operation of portable and automotive navigation systems.
Their design considers radio frequency (RF) optimisation, component durability, and environmental resilience, highlighting the sophisticated engineering behind GPS technology integration.
3. Smart TV

Printed Circuit Boards in smart TVs are pivotal, integrating processors, memory, and connectivity modules like Wi-Fi and Bluetooth within multilayered designs.
These PCBs enable advanced features, including streaming, voice control, and internet browsing, by hosting the TV’s operating system and user interface on microcontrollers or System-on-Chip solutions.
The complexity of smart TV PCBs necessitates specialised repair knowledge, highlighting their crucial role in the functionality, versatility, and user experience of modern televisions.
4. Laptops, Tablets and Computers
Fundamental in laptops, tablets, and computers; PCBs act as the infrastructure for integrating key components like CPUs, GPUs, and memory modules.
The evolution of PCB technology has facilitated the miniaturisation of these devices, enabling sleeker, lighter designs.
Multilayer PCBs in these devices ensure efficient signal routing, minimising electromagnetic interference and enhancing computing performance.
Furthermore, PCBs support modular components, offering upgradability and repairability, crucial for extending device longevity.
This integration and flexibility underscore the essential role of PCBs in modern portable electronics.
5. Printers
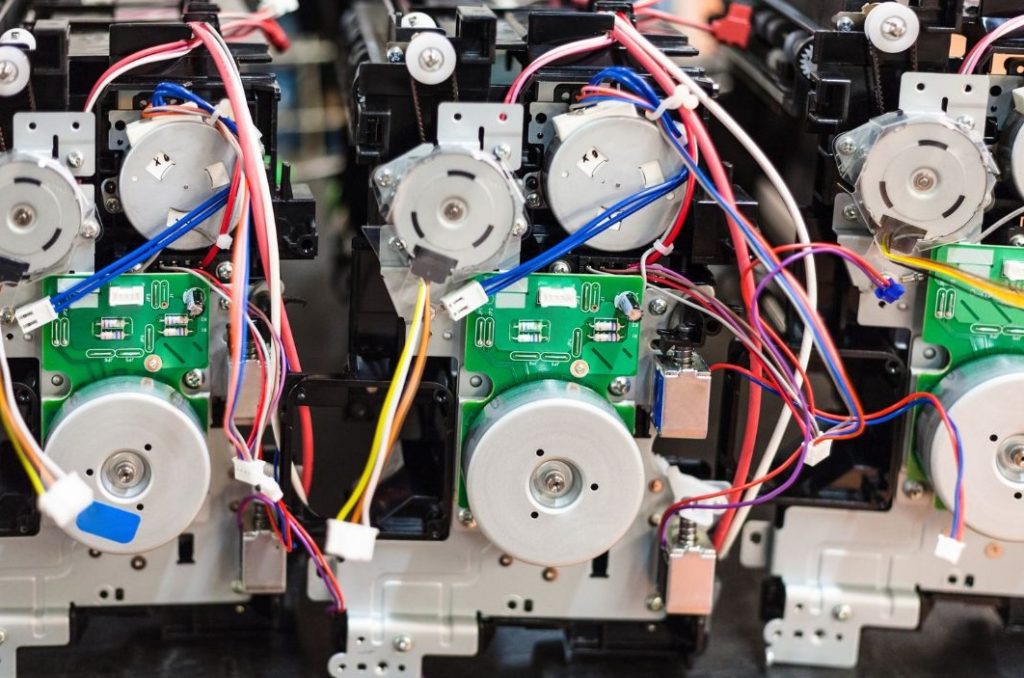
PCBs in printers are integral, managing motors, sensors, and communication interfaces to facilitate efficient printing.
Printers incorporate multiple PCBs for varied functions, including main control, power supply, and interface boards.
Susceptible to faults from electrical surges, environmental conditions, or component wear, diagnosing PCB issues requires tools like multimeters and oscilloscopes.
While some PCB faults can be repaired, extensive damage may necessitate board replacement or professional services, highlighting the critical role of PCBs in printer functionality and maintenance.
6. Washing Machines
Printed Circuit Boards in modern washing machines are pivotal for controlling functions like water intake, temperature, motor control, and cycle sequencing.
Diagnosing PCB issues requires tools such as multimeters, with common faults including component wear, overheating, and corrosion.
Repairing these PCBs demands electronics knowledge, soldering skills, and replacement parts access.
Homeowners must consider repair costs versus new appliance investment, taking into account the machine’s age, parts availability, and warranty, underlining the essential role of PCBs in washing machine operation and maintenance.
7. Refrigerators
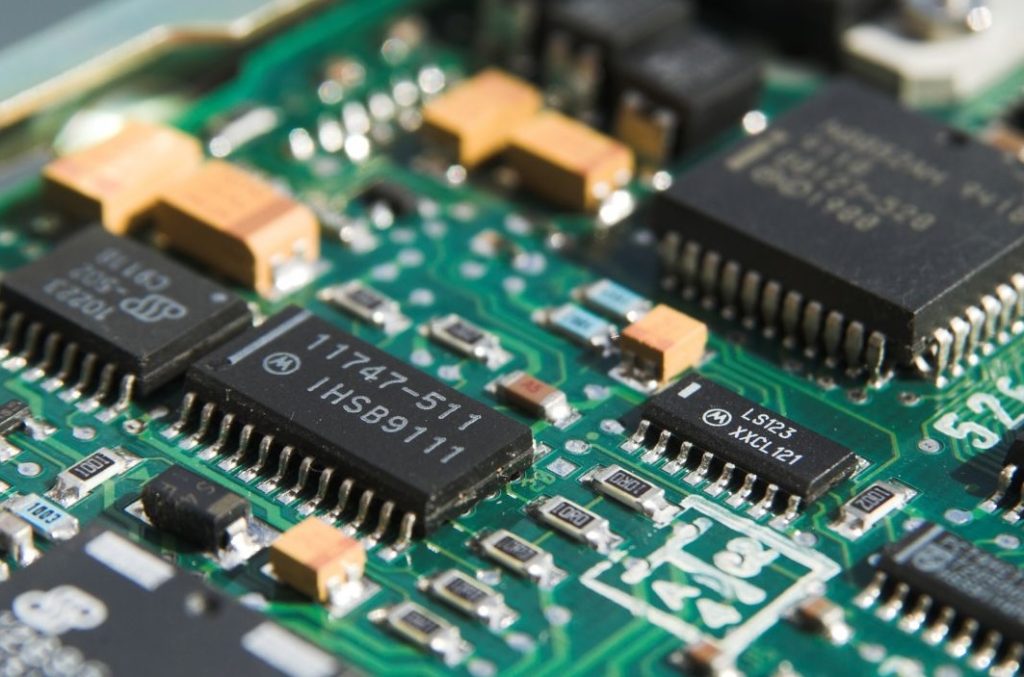
PCBs in fridges are essential for managing temperature, defrost cycles, compressor function, and user interfaces.
Troubleshooting involves multimeters and circuit testers to identify issues like damaged components or relay failures. Safety is paramount; always disconnect power before inspections.
Deciding between repairing or replacing a PCB hinges on fault severity and parts availability.
For complex issues, consulting a qualified technician or the manufacturer is advisable, to ensure the fridge’s safe and efficient operation. This highlights PCBs’ critical role in fridge functionality and maintenance.
8. Smart Watches
PCBs in smartwatches ingeniously pack multiple functionalities into a diminutive space, utilising advanced miniaturisation to integrate microcontrollers, sensors, and power management circuits.
These boards facilitate Bluetooth connectivity, heart rate and GPS tracking, optimising performance while minimising interference.
Emphasising power efficiency, smartwatch PCBs incorporate low-power components and software to extend battery life.
Designed to resist moisture and shocks, they employ protective coatings and rugged components, ensuring durability.
The intricate integration within the smartwatch’s compact design underscores the balance between functionality, reliability, and user experience.
9. Vacuum Cleaners

PCBs in vacuum cleaners are crucial for controlling motor speed, power distribution, and processing sensor data, acting as the operational core.
They integrate sensors to optimise cleaning performance by detecting obstacles, adjusting suction power, and measuring dust levels.
Additionally, PCBs manage power efficiently, incorporate safety features to prevent overload and handle user interfaces like displays and touch panels.
They also store diagnostic data and facilitate firmware updates, aiding in troubleshooting and enhancing vacuum cleaner functionality and longevity.
Understanding PCBs’ role is key for users and technicians alike.
10. Cameras
PCBs in cameras are essential, supporting components like image sensors and processors within compact designs.
They ensure functionality and performance through meticulous component placement and routing, maintaining signal integrity for high-resolution captures.
Cameras use grounding and shielding in PCB design to reduce noise and enable advanced features such as autofocus and wireless connectivity.
Designed for durability, PCBs in cameras use quality materials and protective measures against environmental damage, highlighting their critical role in camera functionality and reliability.
Understanding the role of electronic PCBs is essential for professionals in the electrical, engineering, and product design fields.
If you seek further information or wish to discuss how PCBs can enhance your projects, please do not hesitate to contact us here at Altimex for all your PCB needs.